|
ORIGINS OF CIVILIZATION
TIMELINE |
|
The
First Pots |

The researchers
are confident that they have dated the earliest pottery from
the site to 20,000 to 19,000 years ago, several thousand years
before the next oldest examples. “These are the earliest
pots in the world,” says Harvard’s Ofer Bar-Yosef,
a coauthor on the Science paper reporting the finds. He also
cautions, “All this does not mean that earlier pots will
not be discovered in South China.” |
|
Traces
of 10,000-Year-Old Rice Beer Found in China |
|
|
Oldest
Mummies
Meet the Chinchorro mummies, the oldest
ones in the world |
|
|
Scientists
discover oldest evidence of bread
2018 |
Until now, the oldest evidence of bread came from
Turkey; those finds are 9,000 years old.
Scientists
have discovered the earliest known evidence of bread-making,
from a 14,000-year-old dig site.
The bake would
have looked like a flatbread and tasted a bit like today's multi-grain
varieties, they say.
Our ancestors
may have used the bread as a wrap for roasted meat. Thus, as
well as being the oldest bread, it may also have been the oldest
sandwich.
The find,
from the Black Desert in Jordan, pushes back the first evidence
for bread by more than 5,000 years. |
|
OLDEST
SANITATION SYSTEM |
Rather than growing
organically, Harappan settlements were laid on a similar grid
pattern, with large communal buildings and the world’s earliest
sanitation system—a degree of urban planning not to be seen
again in the subcontinent until the 18th century, when Sawai
Raja Jai Singh laid out plans for the "pink city" of
Jaipur. Brick houses, some multi-storey, opened only to inner
courtyards and smaller lanes. Each house had access to covered
drains along the main roads, suggesting a fairly egalitarian
society. The Harappans also had granaries, dockyards, reservoirs,
irrigation canals and public baths. |
|
Were there mummies in Bronze Age Britain?
Bone analysis suggests the practice was common in ancient Britain
2015 |
Tightly wrapped
mummies conjure up images of ancient Egypt, but very few people
would think of ancient England. Now, scientists have presented
evidence that the practice of preserving bodies might have been
widespread in the Bronze Age Britain, from 2500 B.C.E. to 800
B.C.E. To find out whether the ancient English mummified their
dead, archaeologists examined skeletons from burial sites across
the island and compared them with well-preserved mummies from
Yemen and Ireland (where they were preserved in a peat bog).
Mummification—preserving dead tissue by removing internal
organs and treating the flesh with chemicals or smoke—prevents
bacteria from feasting on the recently deceased. In dry climates,
the flesh stays preserved for centuries. But in the damp soil
of the United Kingdom, even mummified tissue eventually decays.
The bones that remain, however, show no scars from microbial
attack, unlike the skeletons of the unpreserved. A microscopic
analysis of 34 individuals from Bronze Age burial sites across
Great Britain reveals that only some skeletons at each site suffered
bacterial degradation. The remaining bones came from mummified
bodies, the researchers conclude in a paper recently published
in Antiquity (but not yet on the journal's website). Skeletons
buried during other historical periods don't show the same intact
bones, so the phenomenon appears to be unique to the Bronze Age,
say the scientists. "The idea that British and potentially
European Bronze Age communities invested resources in mummifying
and curating a proportion of their dead fundamentally alters
our perceptions of funerary ritual and belief in this period,"
the researchers say in a statement. |
|
Cádiz |
Cádiz,
the oldest continuously inhabited city in Spain and one of the
oldest in western Europe, was founded by the Phoenicians. Cádiz
is sometimes counted as the most ancient city still standing
in Western Europe. The city is dotted with numerous parks where
exotic plants flourish, including giant trees supposedly brought
to Spain by Columbus from the New World. |
|
Eyed
Needles Were Invented around 40,000 Years Ago in Eastern Eurasia,
Archaeologists Say |
|
|
The Development of Agriculture
The development
of agriculture about 12,000 years ago changed the way humans
lived. They switched from nomadic hunter-gatherer lifestyles
to permanent settlements and farming.
|
In Mexico,
squash cultivation began around 10,000 years ago, but corn (maize)
had to wait for natural genetic mutations to be selected for
in its wild ancestor, teosinte. While maize-like plants derived
from teosinte appear to have been cultivated at least 9,000 years
ago, the first directly dated corn cob dates only to around 5,500
years ago.
Cattle (Bos
taurus), goats (Capra hircus), sheep (Ovis aries), and pigs (Sus
domesticus) all have their origins as farmed animals in the so-called
Fertile Crescent, a region covering eastern Turkey, Iraq, and
southwestern Iran. This region kick-started the Neolithic Revolution.
Dates for the domestication of these animals range from between
13,000 to 10,000 years ago. |
|
Expansion of farming in Western Eurasia 9600 to
4000 BCE |
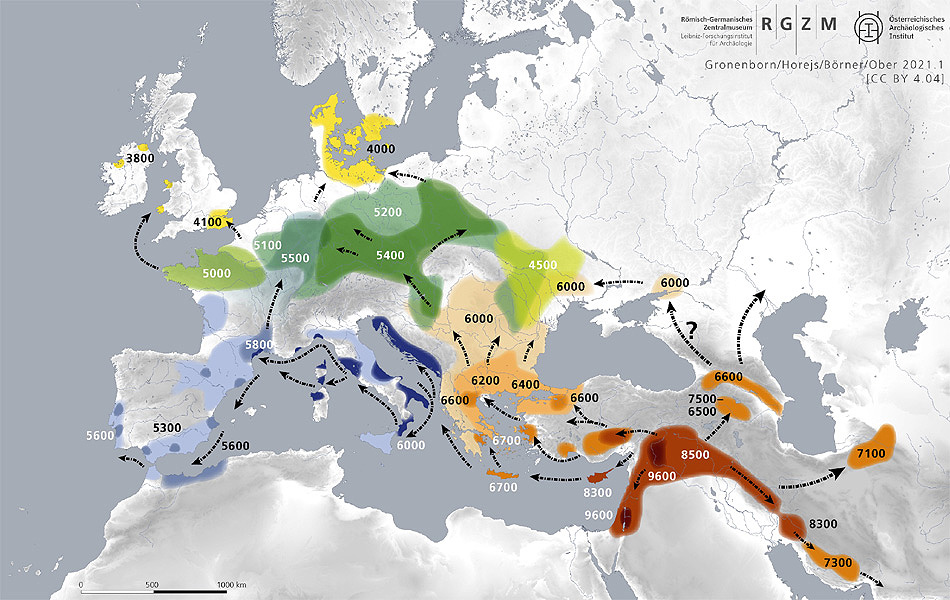
|
|
Were
the Azores home to an ancient civilisation?
BBC REEL |
|
|
7,000-Year-Old
Canoes Reveal Early Development of Nautical Technology |
 |
|
ANCIENT
OIL LAMPS HISTORY |
|
|
The
oldest golden treasure in the world |
The oldest golden treasure
in the world excavated only in 1972, has not been found in Mesopotamia
or Egypt, the earliest written civilizations in human history.
To everyone's surprise, it was discovered in northeastern Bulgaria,
near the attractive, modern city of Varna and is more than 6,000
years old. |
|
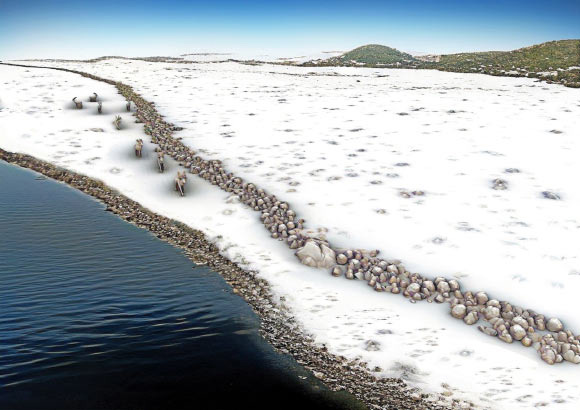
Stone
Age Hunting Megastructure Discovered in Baltic Sea
A team of
archaeologists from Germany has discovered a submerged Stone
Age megastructure in the Western Baltic Sea at a water depth
of about 21 m. The structure was likely constructed by hunter-gatherer
groups more than 10,000 years ago and ultimately drowned around
8,500 years ago; since then, it remained hidden at the seafloor,
leading to a pristine preservation that will inspire research
on the lifestyle and territorial development in the larger area. |
 |
|
Homo
sapiens Reached Northern Europe by 45,000 Years Ago, Scientists
Say |
|
|
Researchers
find the earliest evidence of domesticated maize |
|
|
The
Origin of Cultivation and Proto-Weeds, Long Before Neolithic
Farming |
|
|
List
of oldest buildings in the Americas |
|
|
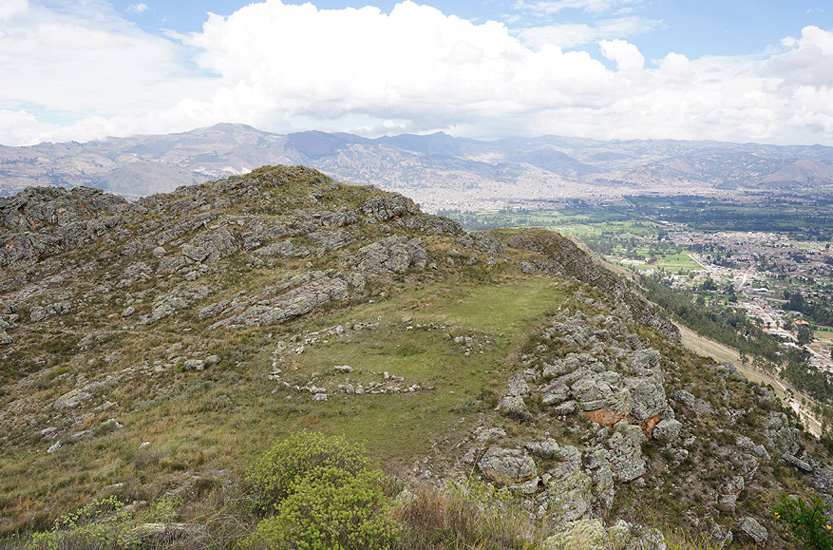
CALLACPUMA
4,750-Year-Old Monumental Stone Plaza
Discovered in Peru
|

|
A team of anthropologists from the University
of Wyoming, the University of California, Santa Barbara and the
University of New Hampshire has discovered a 4,750-year-old megalithic
circular plaza measuring 60 feet/18 meters in diameter at Callacpuma
in the Cajamarca basin of Peru. This is one of the earliest known
monumental and megalithic structures in the northern Peruvian
Andes and one of the earliest examples in the western hemisphere. |
|
|
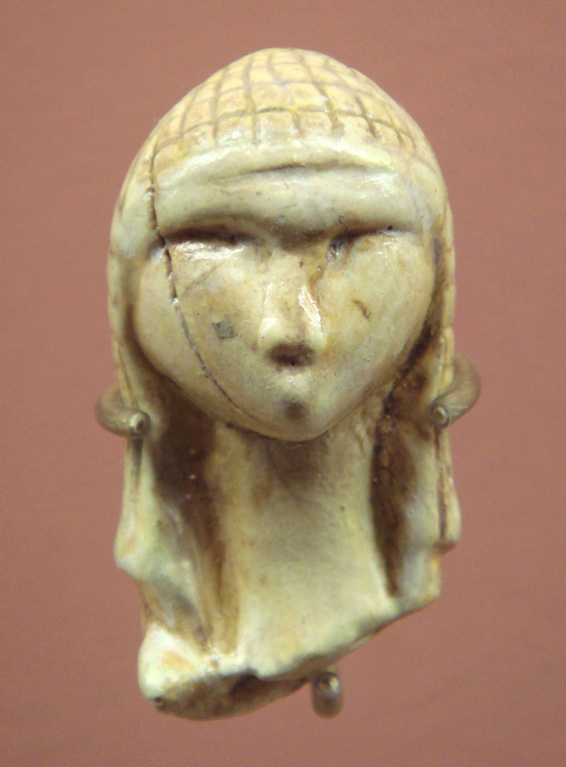
Venus of Brassempouy
About 25,000
years old, it is one of the earliest known realistic representations
of a human face. |
 |
|
Modern Humans With Bows and Arrows Invaded
France 54,000 Years Ago
|
Around 54,000
years ago, a group of anatomically modern humans forayed into
southern France, intruding deep into the stamping ground of Neanderthals.
And they came prepared, bearing the first bow and arrow technology
to reach Europe – a good 10,000 years earlier than we assumed.
Not that it helped them survive. |
|
Neanderthals
Created Stone Tools Held Together by Ochre-Based Adhesives, Scientists
Say |
|
|
Lahuradewa,
India |
The site is
noted to have been occupied as early as 9,000 BCE,and by 7,000
BC it provides the oldest evidence of ceramics in South Asia.
Excavations
reported one of thw earliest archaeological sites in the world
for cultivation of rice, with Lahuradewa Period IA giving samples
that were dated by AMS radiocarbon to the 7th millennium BC |
|
The Indus Valley civilisation is 2,500
years older than previously believed
May 30, 2016
|
The Indus Valley civilisation may be even older
than initially thought.
A group of
researchers in India have used carbon dating techniques on animal
remains and pottery fragments to conclude that the Indus Valley
settlements could be 8,000 years old—2,500 years older than
previously believed |
|
Chopani Mando |
Remains of
pottery and rice have been found from 7000-6000 BC
Chopanimando
is an important archaeological site, which indicates transition
of humans from food gathering society to food production society |
|
History of Rice
Cultivation |
The current
scientific consensus, based on archaeological and linguistic
evidence, is that Oryza sativa rice was first domesticated in
the Yangtze River basin in China 13,500 to 8,200 years ago. From
that first cultivation, migration and trade spread rice around
the world - first to much of east Asia and then further abroad
and eventually to the Americas as part of the Columbian exchange. |
|
The earliest
recorded metal employed by humans appears to be gold, which can
be found free or "native". Small amounts of natural
gold have been found in Spanish caves dating to the late Paleolithic
period, 40,000 BC |
|
|
Certain metals,
notably tin, lead, and at a higher temperature, copper, can be
recovered from their ores by simply heating the rocks in a fire
or blast furnace, a process known as smelting. The first evidence
of this extractive metallurgy, dating from the 5th and 6th millennia
BC, has been found at archaeological sites in Majdanpek, Jarmovac
and Plocnik, in present-day Serbia.To date, the earliest evidence
of copper smelting is found at the Belovode site near Plocnik.
This site produced a copper axe from 5,500 BC, belonging to the
Vinca culture. |
|
|
NOTES
TO VERIFY |
There was
indeed contact during what we call “ prehistory “.
Genetic evidence ( and physical evidence) suggests that ancient
humans from the Japanese islands traveled down the west coast
of America several thousands of years ago. Physical evidence
of that journey was left in the Channel Islands and in Peru.
Additionally, a 5 thousand year old “rocker” skull
was discovered in a cave in Brazil. The skull is a direct link
to the South Pacific Islanders. Chickens came from those travelers
from the South Pacific. These are just the tip of the iceberg
when it comes to ancient contact. Tobacco and coca leaves were
discovered in an Egyptian pharaohs tomb. Both of those items
are indigenous to the “New world” exclusively. |
|
|





